There’s a fine balance when it comes to setting your prices. You don’t want to alienate all your customers, but simultaneously, you want to maximise revenue. That’s where price elasticity of demand (PED) comes into play.
By calculating price elasticity of demand, you can make informed decisions when setting your prices. So, if you want to learn more about how price elasticity works and affects your small business, keep reading.
What is price elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand is a formula to determine how sensitive your customers are to changing prices. The formula helps you understand how much your sales volume will change if you adjust the price.
This means, before making permanent pricing adjustments, you can decide whether the change is financially viable or justifiable.
Price elasticity of demand formula
You can use the following formula to calculate price elasticity of demand:
Price Elasticity of Demand = Percentage Change in Quantity Demanded / Percentage Change in Price
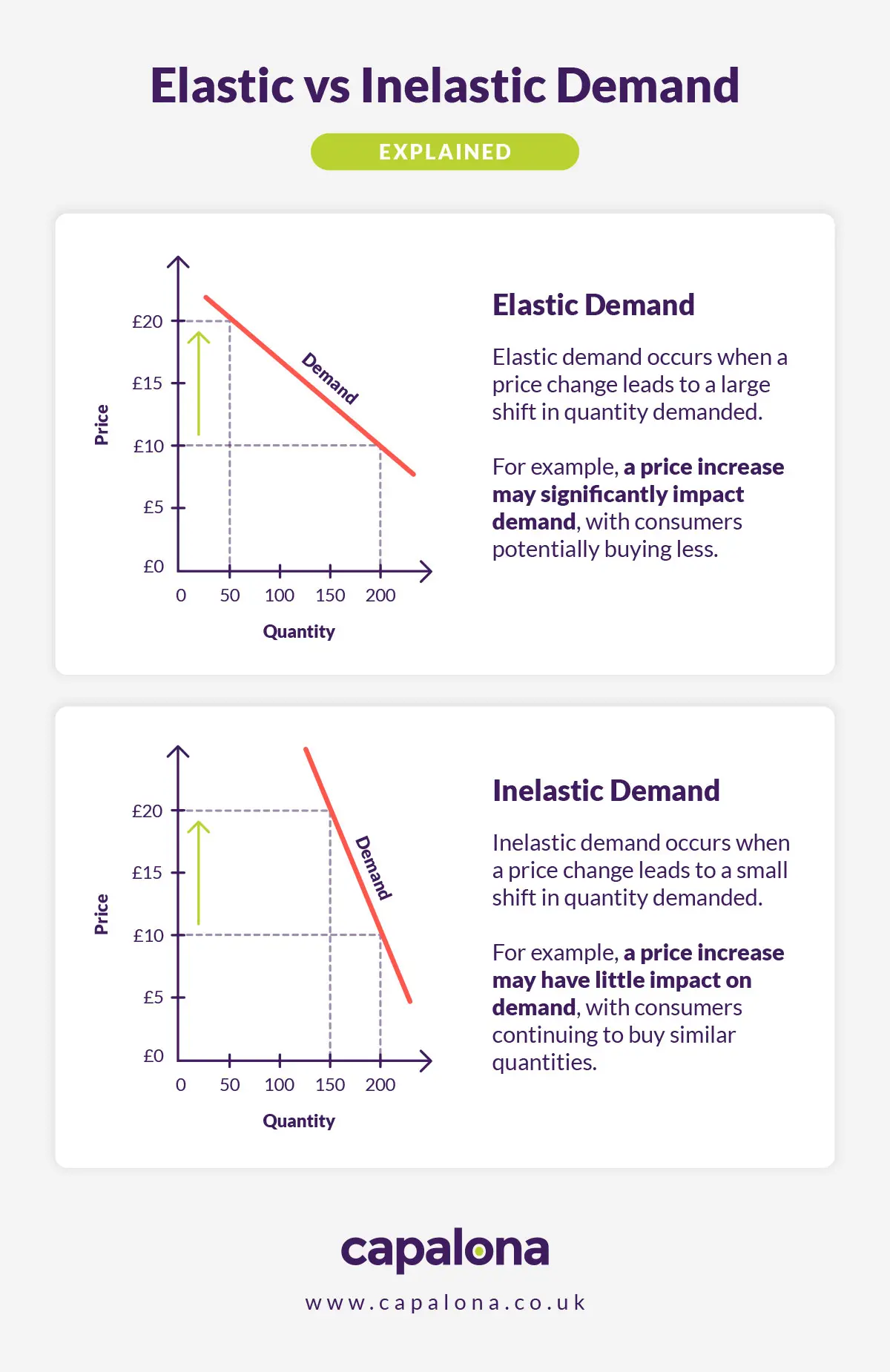
Elastic vs inelastic pricing
If price elasticity of demand is MORE than 1: Demand is elastic, therefore customers are very sensitive to price changes.
If price elasticity of demand is equal to 1: Demand is unit elastic, therefore revenue remains unchanged regardless of price changes.
If price elasticity of demand is LESS than 1: Demand is inelastic (customers are less sensitive to price changes)
The more elastic your price, the more sensitive your customers are to price changes, so any small change in price can cause a substantial drop in revenue. But, having elastic pricing can also be a good thing. You know customers are sensitive to price changes, so if you were to drop pricing to drive new product launches, there’s a good chance customers will buy more.
Whereas, with inelastic pricing, your customers aren’t as sensitive to pricing changes, which can mean there are little to no good alternatives to the product you’re selling, effectively creating a captive market.
An example of price elasticity of demand
Let’s say you run an online luxury clothing store. You currently sell 30 units of a particular piece of clothing for £100 each week. You increase the price by 15% to £115. You notice sales drop by 10% to 27 each week.
Price elasticity = -10% / 15% = 0.6
In this example, demand is inelastic, which means your customers are less sensitive to price changes. So you can confidently increase your pricing without affecting demand too much.
Three factors that influence price elasticity of demand
There are many factors that can influence your price elasticity of demand, here are just three:
- Necessity vs luxury. Basic items of necessity are usually inelastic. This is because they are necessary products, so customers don’t have much choice but to pay what you charge. Whereas, luxury items, like furniture or home decoration items, can be elastic. Customers can simply choose not to purchase the items while pricing is high.
- Availability of substitutes. If your products or services are competing in a saturated market with many alternatives, customers can easily purchase the same goods elsewhere, which means pricing is elastic.
- Brand loyalty. If you focus on building strong brand loyalty, e.g. delivering a personalised experience or exceptional customer service, pricing can be inelastic. Customers are likely to remain loyal to your brand, even if you do increase pricing.
Common pitfalls to avoid when calculating PED
There are a few things you might want to avoid when calculating price elasticity of demand:
Don't rely on historical data
Just because your last calculations said your pricing was inelastic doesn’t mean to say it can’t change. Market conditions change, and customer behaviour changes, you need to account for this before diving headfirst into permanent pricing changes.
Don’t fail to segment your audience
An older demographic might respond differently to pricing changes than younger demographics. That’s why it’s important to calculate price elasticity of demand in segments. One group might have more disposable income than another, so they’re unlikely to move to a different brand should you increase your prices.
Don’t forget to acknowledge seasonal fluctuations
You don't want to assume your changes in revenue are exclusively the result of new pricing strategies being put in place. Other factors, such as seasonality, may be playing a big part in customers' spending habits at different times of the year.

Financial solutions to help boost cash flow
If you’ve changed your pricing strategy and it’s resulted in lost revenue, even if it's a temporary loss in earnings, you might consider applying for a business loan to help rebalance cash flow and better manage your business finances.
What kind of finance can you apply for?
eCommerce business loans
If you run an eCommerce or retail business, you can apply for an eCommerce business loan or a retail business loan. These loans can be either unsecured or secure forms of finance, which gives you greater flexibility in how you choose to lend. Use the loan as a stopgap to ensure important bills are covered over this period of financial uncertainty.
Inventory finance
If your pricing is elastic, you might find that dropping the price of your item to become more competitive can increase demand for your product. In these cases, you might be short on stock. Inventory finance can be used to bulk-purchase inventory to take advantage of cost savings and promptly fulfil customer demand.
If you don’t want to purchase stock, that’s no problem. You can use your inventory as security to lend against, freeing up some much-needed cash to spend on whatever you please.
Merchant cash advance
Merchant cash advance is another option for businesses that take credit and debit card payments. This type of finance is repaid as a percentage each month, which means on the months your revenue is lower, you repay less. This approach to flexible repayments makes the cash advance much more affordable for retail and eCommerce customers — there are no fixed payments to worry about.
Ready to compare business finance options? Find and compare lenders for free with our self-serve loan comparison tool. Start your business finance journey.






